An organizational unit (OU) is similar to a folder that subdivides and organizes network resources within a domain.
An OU can contain other OUs and any type of object type, such as users, computers, and groups. OUs can be nested to logically organize network resources.
Parent OUs are OUs that contain other OUs. Child OUs are OUs within other OUs. The recommended maximum nested level of OUs is five. Too many levels of nested OUs can slow resource requests and complicate group policy application
OUs are typically organized by the following:
-
Physical location, such as a country or city
-
Organizational structure, such as the HR, sales, and IT departments
-
Object types, such as user accounts or computers
-
Hybrid of location, organizational structure, and object type
Group Policy: One of the main reasons to use OUs to store objects instead of containers is the application of the Group Policy. Create OUs for each set of objects that needs to have different Group Policy settings. Keep in mind:
Group Policy Objects (GPOs) can be linked to OUs. Policy settings within a GPO apply to all objects within the linked OU. Through inheritance, settings applied to the domain or parent OUs apply to all child OUs (and to all objects within those OUs).
A default container is not an OU and cannot have GPOs linked to it. A good practice is to move objects out of the default containers and into an OU. For example, you can move computers out of the Computers container and into an OU of your choosing, where Group Policy can be applied.
Preventing Accidental Deletion : Objects in Active Directory can be accidentally deleted using Active Directory Users and Computers and other management tools. The following types of deletions are the most common:
Leaf-node deletion occurs when a user selects and deletes a leaf object. A leaf object is an object that cannot contain child objects. Leaf objects are also referred to as subordinate objects. Organizational Unit (OU) deletion occurs when a user selects and deletes an OU. Deleting the OU deletes all objects within the OU (including any child OUs and their objects).
When you create an OU using Active Directory Users and Computers, the Protect container from accidental deletion option is selected by default. You can turn the option on or off after the OU is created in one of the following locations:
On the Object tab of the OU in Active Directory Users and Computers. Select Advanced Features from the View menu before opening the Object tab. On the Security tab in Computers or Active Directory Sites and Services.
Delegating Authority: Delegating authority is the assignment of administrative tasks--such as resetting passwords or creating new users--to appropriate users and groups. You should set up the OU structure in a way that best facilitates your support plan. Be aware of the following facts about delegating control:
Using the Delegation of Control wizard or the Authorization Manager console, you can delegate control of any part of an OU or object at any level. An object-based design allows you to delegate control based on the types of objects in each OU. For example, you can delegate control over specific object types, such as user objects. A task-based design allows you to delegate control based on the types of administrative tasks that need to be done. Some examples of administrative tasks are:
User account management, such as creation and deletion Password management, such as resetting and forcing password changes Group membership and permissions management
How to create an OU :
-
Login to your domain controller with administrative privileges.
-
Navigate to Start → Administrative tools → Active Directory Users and Computers.
-
Right-click on the domain name and select New > Organizational Unit.
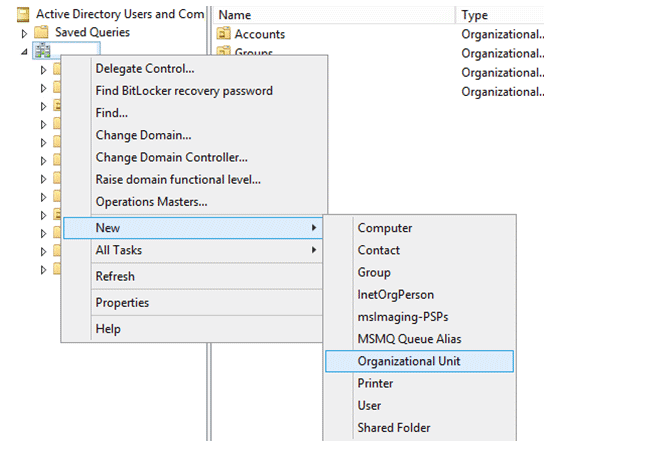
Specify the name of the OU to create. you can tick mark the accidental protection deletion to prevent the OU from accidental deletion.
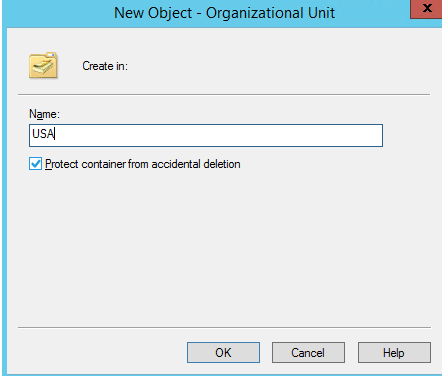
How to delete an OU :
-
Login to your domain controller with administrative privileges.
-
Navigate to Start → Administrative tools → Active Directory Users and Computers.
-
Click View on the menu bar, and then click Advanced Features.
-
Navigate to the OU that you want to delete, right-click on it and click on Properties.
-
Click the Security tab → Advanced
-
In Permission Entries, if the Deny entry option has been selected for everyone, remove it. (referral)
-
Click OK to close the Advanced Security Settings.
-
Navigate to the Object tab and uncheck the "Protect from accidental deletion" checkbox
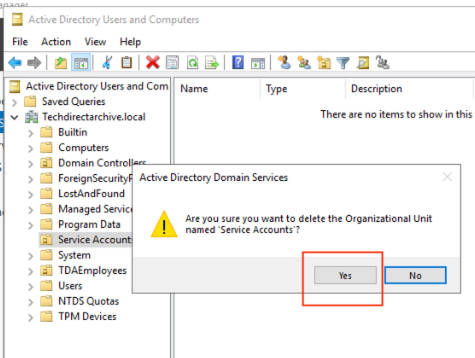
Now you can select the desired OU and delete it.
If you have any issues or questions about , feel free to contact me. Thank you 🌟 for reading ! like , share and subscribe to my newsletter for more !
© Debasish Lenka.RSS